Module 3. Emotion Regulation: (Discussion #2) Understanding Emotions

DBTuesday is a series of posts where we explore skills and concepts from dialectical behavior therapy (DBT).
This is one of several posts focusing on emotion regulation, which is the third module of DBT skills training. See this post for general info about DBT and this post for more info about emotion regulation.
How are emotions helpful?
1) Emotions help us to gain information
- Emotions can alert us to whether something in our environment is helpful or harmful
- Emotions give us information through our body more quickly than what we’re able to get from thinking
- Emotions allow us to connect with Wise Mind (see this post) and have a holistic, intuitive understanding that incorporates both objective and subjective knowledge
- Emotions are stored in memory to help us more easily recognize and respond to similar situations in the future
2) Emotions help us communicate with and influence others
- Emotions can help us convey information not only verbally but also nonverbally through facial expressions, body language, or tone of voice
- Emotional expression can create an automatic response in others and cause them to feel similar to ourselves or respond in ways that help us
3) Emotions help us to react and respond to situations
- Emotions can motivate us to act in situations where we need to act
- Emotions help us to respond quickly to situations where we need to act instantaneously and don’t have time to mentally process it fully
- Emotions help to keep us safe in situations that feel dangerous
Examples of how emotions can be helpful
- Anxiety: can help us prepare for and accomplish valued goals or activities (e.g. getting to work on time, motivation to study for a test)
- Anger: can motivate us to fight for something we value and override feelings of fear or hesitation that might prevent us from acting
- Sadness: can signal to ourselves or others that we need some comfort or time to recover; can evoke feelings of compassion that motivate us to offer help or care
- Guilt: can alert us to something we’ve done that doesn’t fit with our values and motivate us to take corrective action (e.g. apologizing, adjusting behavior)
How do emotions happen?
Emotions are complex and involve the following sequence of events:
1) Prompting event: something happens
- This can be either something in our surroundings or something internal (e.g. memory, thought, feeling)
2) Interpretation: we understand what happened in a certain way
- Different interpretations can lead to different emotions (e.g. “They aren’t talking to me because they’re busy” vs. “They aren’t talking to me because they hate me”)
3) Physical response: our body changes, e.g.
- Muscle tension/relaxation
- Heart rate
- Breathing rate
- Skin temperature/color
- Blood pressure
- Facial changes (e.g. clenched jaw, tension in cheeks/forehead/eyes, grinding teeth, smiling/frowning)
4) Action urge: we might have a desire to do something (e.g. wanting to yell)
5) Expression: we might perform a behavior based on that desire (e.g. actually yelling)
What types of emotions are there?
Being able to identify emotions can help with managing them. Here are a few different lists of emotions as a reference point.
6 basic emotions (Paul Ekman, 1972)
/an-overview-of-the-types-of-emotions-4163976-01-474bb455cfe74c3cb98ea46113e3108b.png)
What each emotion feels like:
- Happiness = contentment, joy, satisfaction, well-being
- Sadness = disappointment, grief, hopelessness, disinterest
- Fear = sense of danger, fight-or-flight response, anxiety
- Disgust = aversion, repulsion, loathing (can be physical disgust or moral disgust)
- Anger = annoyance, frustration, bitterness, rage
- Surprise = brief shock, focused attention on something sudden or unexpected
Signs of each emotion:
- Happiness = smiling, relaxed posture, upbeat speech
- Sadness = crying, tiredness, quietness, withdrawal
- Fear = wide eyes, trying to hide or flee, rapid breathing, increased heart rate
- Disgust = turning away, retching, wrinkled nose, curled lip
- Anger = frowning, glaring, turning away, gruff speech, yelling, sweating, turning red, hitting, throwing objects
- Surprise = wide eyes, raised eyebrows, jaw open, jumping back, gasping, screaming
8 basic emotions (Robert Plutchik, 1980)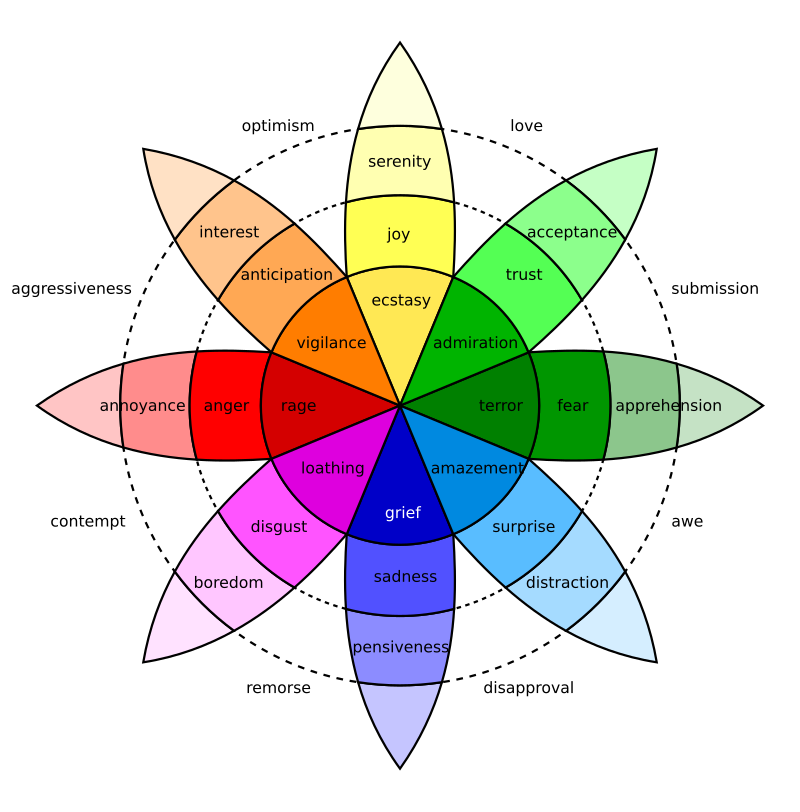
This model has four pairs of opposite emotions:
- Joy vs. sadness
- Anger vs. fear
- Trust vs. disgust
-
Surprise vs. anticipation
These emotions are arranged into a wheel:
- Each basic emotion can have different levels of intensity; more intense emotions are closer to the center
- Some basic emotions are more similar to one another; similar emotions are closer together on the wheel
- Additional feelings can be described based on combinations of basic feelings (e.g. love = joy + trust)
27 categories of emotion (Alan Cowen & Dacher Keltner, 2007)

Researchers had participants watch over 2,000 short videos with varied emotional content and describe how they felt while watching. Statistical analysis performed on these descriptions found that they corresponded to 27 distinct emotions.
Reflection
Think about an emotion you’ve experienced that is unpleasant. What might be the purpose behind that emotion (i.e. information, communication, motivation)?
Sources:
https://sunrisertc.com/dbt-emotion-regulation-skills/
https://sunrisertc.com/emotions-list/
https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/emotion-regulation-dialectical-behavior-therapy-dbt-0318135
https://dbtselfhelp.com/dbt-skills-list/emotion-regulation/
https://dbtselfhelp.com/dbt-skills-list/emotion-regulation/what-good-are-emotions/
https://dbtselfhelp.com/dbt-skills-list/emotion-regulation/identifying-describing-emotions/
https://www.verywellmind.com/an-overview-of-the-types-of-emotions-4163976
https://online.uwa.edu/infographics/basic-emotions/
https://www.paulekman.com/universal-emotions/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Plutchik
https://www.pnas.org/content/114/38/E7900

@QuietMagic
*dances* 😛 first one to comment again!! 😀
Think about an emotion you’ve experienced that is unpleasant. What might be the purpose behind that emotion (i.e. information, communication, motivation)?
well XD one emotion I absolutely hate is anger and fear 😀
Anger: motivation to get off my lazy butt XD I am more likely to exercise when angry so I don’t explode around people.
Fear: I worry 😀 yesterday i found out i have been around 3 people who tested positive for Covid and I’ve been near an immune-compromised person in the past few days, and i worry for their health.
also, one thing i found when i am in a fear mood is shallow breathing so a basically barely breathe (only in extreme cases) 😀
@emotionalTalker2260
Hey, thanks for commenting! 😊
What would you say is the cause of the anger? It sounds like once it does occur, you're able to channel that energy in a way that feels useful (e.g. being more active, exercising).
Sorry about everyone testing positive for COVID. 😟 It sounds like the fear serves a purpose there of alerting you to something bad/dangerous and motivating you to protect yourself (or if possible try to offer care to the people that you're worried about).

@QuietMagic
:0 of course I’d comment 🤭 someone has to right (?) and i was more than happy to do so😮 and *~* yeah, when I’m angry, i like to just throw myself into the pool as that cools me down (temperature wise and emotionally) so yeah 😃 and because of a covid scare, I am back to isolating myself away from my family just because. smh.

Unpleasant?
Me having to be outta body with people, places, things. Uncomfortable.
@alleywood13
By out of body, do you mean like you have dissociative episodes where you feel like you aren't yourself? (If so, that's usually a stress/trauma reaction trying to keep things safe. More info HERE.)
